SQLcl Alias Example For Dropping Multiple Objects.
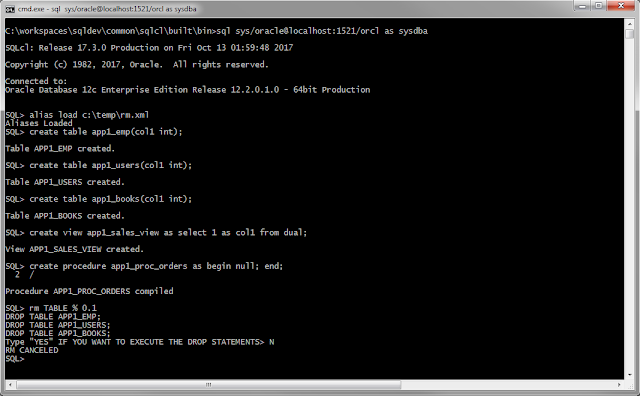
SQLcl allows you to define "named" scripts or statements using the ALIAS command. Jeff has a neat example on his blog . I created the following alias to make it really easy to destroy a database! drop objects. RM Alias Dropping tables, views, procedures is a daily occurrence for database developers. The following SQLcl ALIAS may come in handy when you want to drop lots of objects at the same time. Just specify the object_type : TABLE, VIEW, PROCEDURE, .... object_name: Using a LIKE expression. Example: MY% created: Number of days. Example: 1 A script is written with all the objects listed. The list of objects can be reviewed and an option to execute the script or cancel without dropping anything is provided. Needless to say you can do a lot of damage dropping database objects and this makes it very easy to do so. So use at your own risk! Best to grab the alias code below and see if you can tweak it to suit yourself. Test Env create t...